Key takeaways
-
- Market research reveals the strengths and weaknesses of your project and it’s essential for successful investor pitching
- It saves your time and money, helps with choosing the promotion approach, and may even tell you that your startup needs to pivot
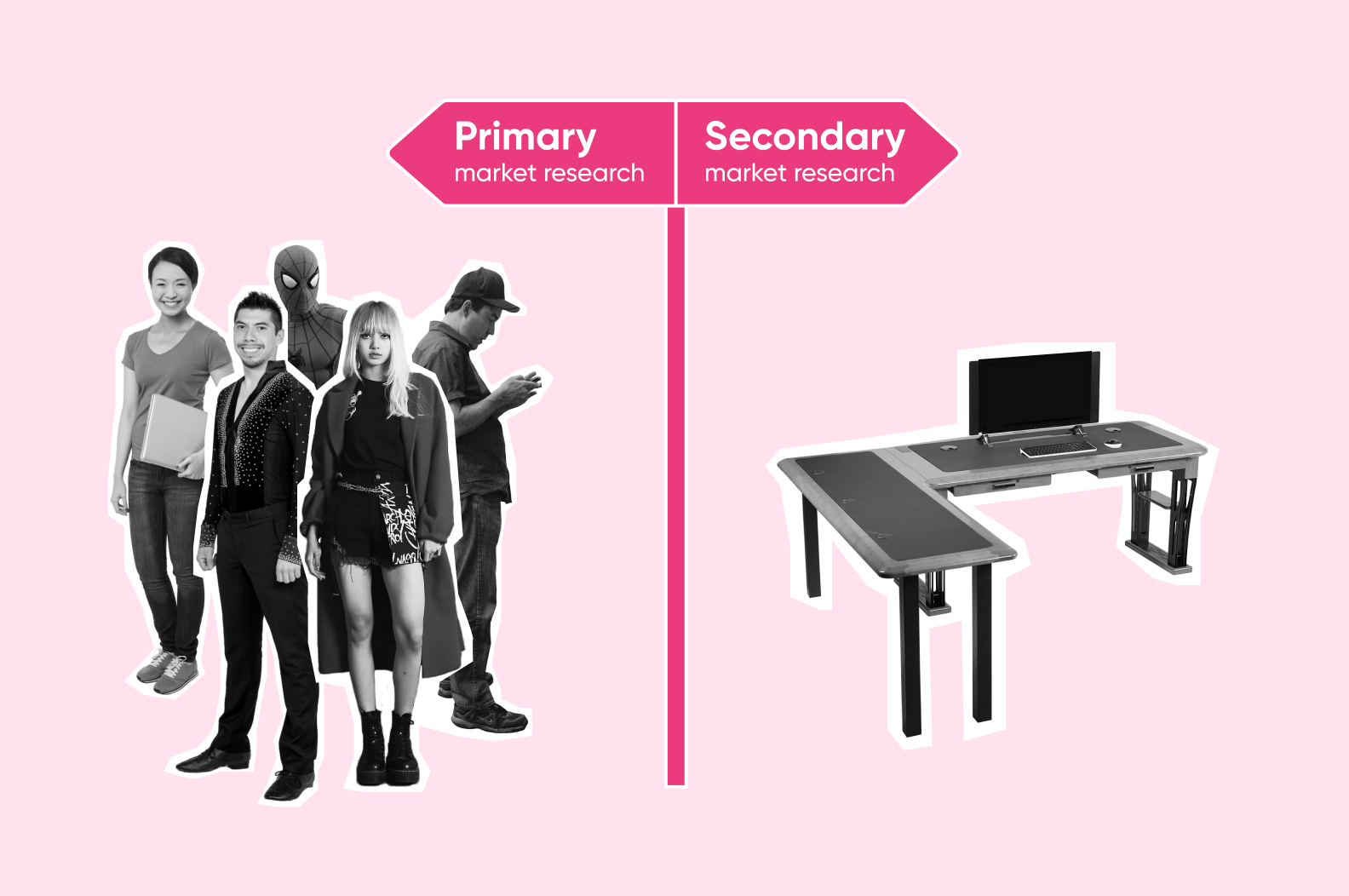
- Market research can be primary, which uses data directly from your target audience, and secondary, which uses existing data from reports
- Market research is typically done before developing an app, but it can be conducted even after launch.
What is market research in the realm of startups?
Market research is a manner of pre-emptively exploring and evaluating the market your startup is planning to join. Sufficient market research brings a clear idea of your project’s perspectives, strong suits, and weaknesses. Supporting your decisions with market research is essential to a successful investor pitch and subsequent launch.
Startups conducting market research use data to:
-
- Examine trends in the market and in the industry. Will you generate the desired revenue after investing in the industry? How big or small is your market? What segment is it possible to occupy?
- Review market dynamics and carefully time your startup’s arrival accordingly. Are there promising trends or technologies? Maybe there are major changes in the overall approach in the market? How do you turn them to your advantage?
- Find your target audience and study their buying behavior. Are there enough clients for your product or service? What’s their age, location, etc.? What is their economic situation ?
- Identify and examine direct and indirect competitors of your startup. How many are there? What market strategies and price points do they have? How much money and effort will it require to rise above the competition?
- Test the demand for your product or service. Do people like your offering? Will they buy it?
It’s also necessary that market research precedes a mobile app business plan.
What’s the significance of market research for a startup?
Market research serves a dual purpose. It allows you to avoid mistakes while ensuring a successful outset of your project.
Market research is a critical business instrument. As such it has several benefits. To begin with, it will preserve your time and money. Market research streamlines the process of finding the product-market fit and ensures that a business idea is feasible. Amongst the most frequent reasons why startups fail is a lack of demand. Gathering data in advance will stop you from pursuing a shaky idea.
Market research attracts investors as well. Supporting your startup project with data will work in your favor. Market research will demonstrate that your business idea has potential, and it indicates that your entire approach is thorough.
Market research can show that strategic changes are necessary. It means your findings may suggest your startup needs to pivot. Let’s say your concept is a groceries delivery startup. But before exploring this concept in full, you commit to surveying your audience. Maybe the market research shows that your future consumers are satisfied with what already exists, but their problem is that they want a better delivery method for the product itself. Taking the information into account, you can decide to scrap the initial project and pivot to a discovered direction. That’s how market research for a startup prevents judgment errors and dead-ends.
Finally, market research affects the promotion approach. Understanding your target market and clients well enough, you’re able to adjust the marketing strategy. Maybe you’ll discover that your potential buyers are predominantly car drivers. Market research showed they also live in large cities with busy traffic. Combining these two factors, your marketing team may opt for billboards.
What types of market research are there for startups?
Typically, you can do two types of market research for a startup, depending on how you gather data. If the information comes directly from your audience and you collect it on your own — it’s considered primary market research. This includes surveys and expert interviews. If you analyze already available data provided in reports or elsewhere, it’s considered secondary market research. One example of this is public databases.
Let’s explore primary and secondary research in detail.
Primary market research
Primary market research is also referred to as ‘field research’, since you speak to someone directly. You should find industry experts and regular users, prepare questionnaires, then interpret and parse data afterwards. And even with professionals’ service, primary market research requires time.
Ways to perform primary market research:
-
- Personal interviews. Video-call conversations or real-life ones help you get to know your audience better, ask additional questions and also refine answers if needed.
- Focus groups. When using this methodology, bear in mind that some people may feel uncomfortable in the group setting. This means they may not as easily express their opinions.
- Surveys, polls, and questionnaires. Are a convenient method to reach an audience online via quantitative research.
- Observation. An expert analysis of consumer’s reaction to your app or service and interaction with it in real-time. Only applicable if an MVP or a full-fledged product is ready.
Primary market research methods belong to one of the two groups: qualitative research and quantitative research. Methods from the former answer how and why people do something, the latter show how much, how often, and who does it.
How is primary market research beneficial?
This method delivers an understanding about your target audience straight from themselves. Market research is a way to learn more about competitors as well. Imagine your startup project is a booking service, so Airbnb and Booking.com appear to be your primary competitors. But after several interviews, you can learn that your target audience resorts to banking apps for hotel reservations. That kind of revelation can drastically change your team’s mindset and influence marketing strategy. There may not be sufficient reports about super-apps usage, but interviewing potential clients can provide the necessary information.
In addition, primary market research can become deeper or more shallow when needed: the available data has no limits.
Secondary market research
Secondary market research’s different name is ‘desk research’, because it’s possible to perform it without leaving the office. Secondary market research is significantly more affordable but only provides other people’s findings. That’s why you yourself should adapt those to your requests. Even more importantly, you should verify data sources’ credibility and avoid others’ unfounded conclusions.
Ways to perform secondary market research:
-
- Evaluate external data. For example, industry analysts’ reports, market surveys, government information, competitors’ data.
- Study internal data. If anyone ran research prior to you, it’s helpful to examine its results.
- Use research programs and technologies. You can run a Google Trends search, use Answer the Public, or other services to learn more about search changes and peaks of interest in the sphere.
How is secondary market research beneficial?
This type of research provides instant results. Also, the information in the reports has been already processed by professionals. Secondary market research can reveal correlations between processes and facts, to help you to understand industry trends better. Often you’re able to easily find the needed information.
Secondary market research covers diverse subjects and underlying surveys are executed on a larger scale. Through Google Trends research, for example, you learn about people’s internet searches not only in the US but all over the world. It means you don’t need to invest millions in interviews with everyone, everywhere to find what you seek.
How to decide on a market research type
If you currently lack substantial research funds or time, opt for the secondary market research since it’s significantly cheaper. But primary and secondary research are beneficial and perform best in combination.
One of the popular approaches is to go from larger concepts to specifics. This means you first conduct secondary market research to grasp the industry trends and existing products. And if this step had a positive outcome, go forward with the primary research to further test your startup idea.
Here’s how this market research process can look with a room booking app. Based on reports you or your teammates examine, you see an increase of interest in traveling and economic growth in the industry. As it’s a positive sign, you proceed to the primary market research. Then your interviews and surveys reveal issues of the target audience that you’re able to solve.
How to do market research for startups in 8 steps
Let’s get straight to the heart of it and find out how to conduct market research for a startup. Go through these eight stages to conduct insightful market research.
Step 1. Specify the objective of the market research
Create a market research plan and decide on the goal you want to achieve. Why do you need it? How will you use the collected data? Determine areas that require special attention. Some typical market research objectives are:
-
- Impressing investors and securing funding. If your app business plan needs real numbers and stats, focus on competitors and industry trends. Your findings should be up to date and relevant.
- Brainstorming a startup idea. If you choose to begin with a problem you can solve rather than a product, focus on the firsthand information. And gathering insights from the audience, explore what other companies are aiming to fulfill this need.
- Proving a concept. If your startup concept is ready, market research is a method of testing its viability.
The following stages are identical for any market research goal. What’s different is the level of attention you give to each stage. And also in the way the results are used: internally or externally. For this article, let’s assume we intend to prove that an apartment booking service we came up with can be successful.
Step 2. Choose the research method
We’ve outlined the two most common methods: primary and secondary market research. These types provide results you can interpret and apply to your product.
Most companies start by conducting secondary market research. It doesn’t take too much of your resources, as you can already access the info online. Primary market research stands in stark contrast: gathering focus groups, recording interviews, and sending out questionnaires are all tedious.
We recommend sticking to the secondary market research in the very beginning. It can provide the answers to most general questions regarding the business niche at first. You can expand on them in primary market research later, and get research data that’s tailored to your startup’s specifics.
Step 3. Explore your market
Start by studying the industry you plan to operate in. Focus on market dynamics and trends. Is it growing? What’s the average life cycle of projects? What’s the total annual revenue of the industry? At this stage, use the combination of primary and secondary research: read industry reports, run Google Trends search and use other instruments, ask experts for their opinion.
Here’s what is helpful to explore at this stage for an apartment booking startup:
-
- How often will people travel in 2024?
- Is traveling on the rise or falling compared to previous years?
- What are the trends in the industry?
- Where do people travel the most?
- Where do they prefer to stay?
Findings at this stage provide a clear direction for the following steps. If you discover that personalized offers are becoming a trend, you’re then able to check how successfully your competitors use them. If you discover that many people book accommodation at the last moment, you can plan to ask about it in interviews.
Step 4. Recognize your target audience
During this step, you define your target market’s demographic while also meeting real users. Here, primary market research is key.
Firstly, outline your target buyer’s persona. Imagine a typical user of your product or service in a determined area. If it’s the initial outline of the buyer’s persona, start by thinking who can pay for your service? What’s their income? Knowing these two factors, estimate their profession and occupation. After that, determine key characteristics like:
Then find candidates for the survey and additionally check if they suit your research parameters. That preparation helps to guarantee your findings’ relevance. If your research is for the booking app, rule out those who never travel or only stay with their friends and family. If your startup will launch in the US, don’t invite people living in Europe, etc.
Here’s what we recommend for conducting interviews:
-
- Prepare open-ended questions. ‘Where do you stay during vacation?’ is a good interview question. And ‘Do you book apartments to stay during vacation?’ is a yes or no question that won’t give you an elaborate answer.
- Use neutral language, don’t lead your subjects in any special direction.
- Question customers about competitors. Explore solutions your target audience prefers.
- Record interviews with consent and take notes for a more in-depth analysis of the information gathered.
Step 5. Examine the competitors
Previously, you learned what companies your audience view as your competitors. The next logical stage in the market research for startups is studying them. To conduct a meaningful study you should determine the competitors belonging to every category:
-
- Direct competitors. It’s the businesses that provide a product or service like yours to a similar target market. For an apartment booking app these are Airbnb, Booking.com, etc.
- Indirect competitors. It’s the businesses that provide a distinct service in your category to a similar target market. Indirect competitors satisfy the same need your startup is seeking to satisfy. In our example, this category includes traditional travel agencies, long-term rental services, etc. depending on how wide you want to go.
- Replacement competitors. It’s companies from completely different categories that can satisfy a similar customer request. What will your audience use to have a vacation apart from previously stated services? Maybe they can buy a tent in a local sports store to stay wherever they plan to.
Limit yourself to 10 or fewer companies — approximately three in each category. That way, you can study all of them carefully. You’ll need to examine their products, prices and general strategy, approach to marketing, and reputation among your consumers. But above all, you should pinpoint their strengths and weaknesses. And then compare your startup idea to existing solutions. How will you differ from them? What potential strong and weak points does your product have?
Step 6. Review the data
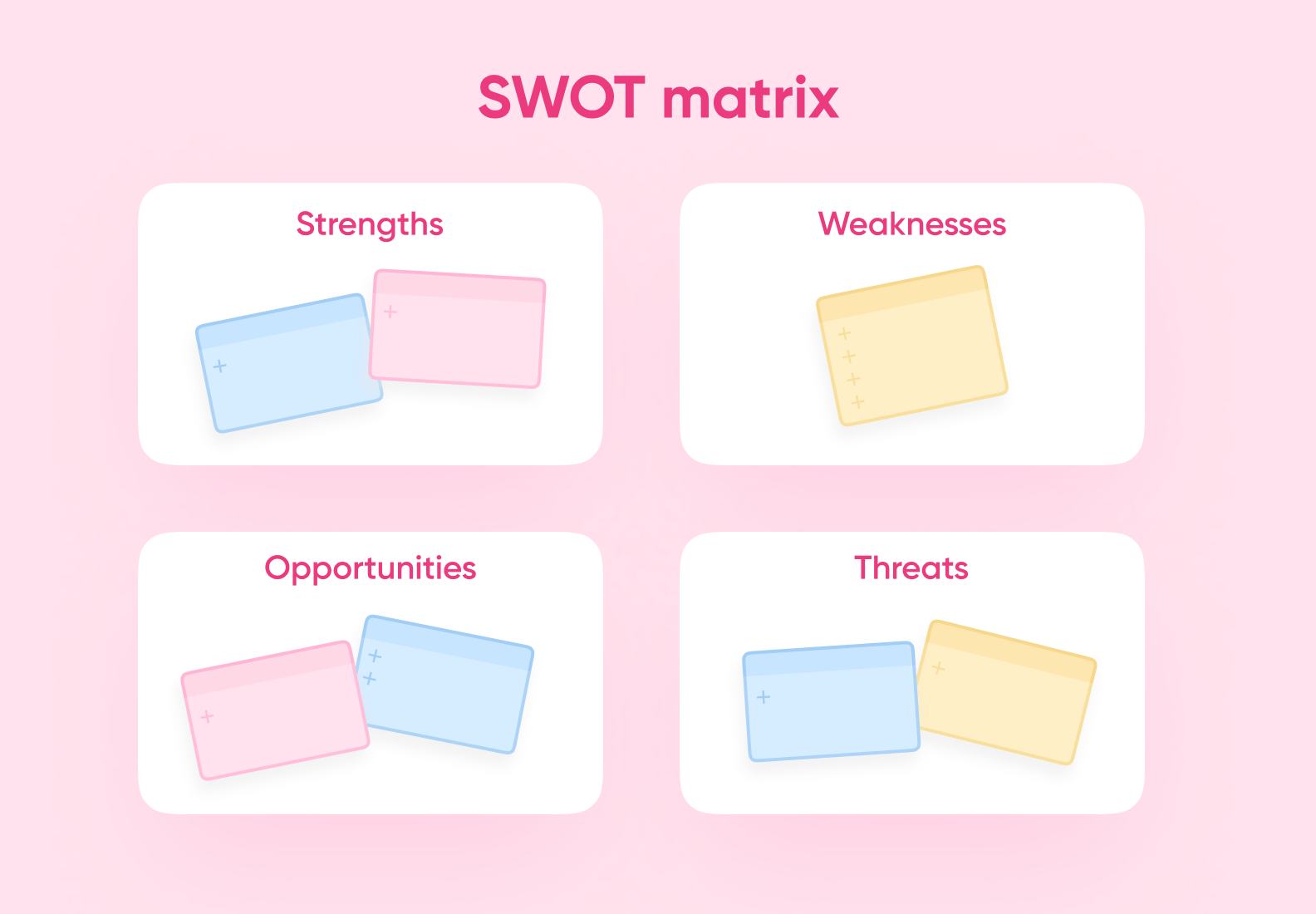
After the market research for a startup idea is done, gather the results and analyze them. We believe it’s convenient to lay everything out in Miro. This way, it’s easy to see correlations and contradictions. Also, it might be helpful to fill in the SWOT matrix.
Based on your research, you may decide to pivot because of market saturation and other factors. Or if you have positive insights, write a draft for a business plan for your mobile app. Either way, from now on you can back up your strategic decisions with data.
Step 7. Notify your team on the key findings
Once you analyze the data, gather key insights and relay them to your team. After everyone’s goals are aligned, create a plan with actionable steps that everyone can follow.
Even if the data isn’t overwhelmingly positive, a realistic approach to development takes uncertainty out of the equation. Your team members will know what solution to include to maximize your startup’s chances of success.
Step 8. Reassess the market if needed
Once you test your MVP and become more in tune with your audience, you can conduct research to understand it even better. Based on these new findings, you can add features or change some things to enhance the user experience.
This is a useful step to take if the market suddenly shifts, or new instruments appear which make market research easier. You can discover trends to use later and pull new clients in. And if the startup doesn’t work, new research can shed light on ways to adjust the existing strategy.
When to do market research for your startup
Market research is most common before developing a brand-new solution. Nevertheless, you can conduct one when your product has already launched. Resort to market research whenever you need new insights from the market.
For example, after discovering their toys cater predominantly to boys, Lego invested in extensive market research with 3,500 girls and their mothers. During the 4 year period, Lego explored what would make their toys more interesting for girls. That resulted in a brand new toy line called ‘Friends’. Constant research only helps your startup to iterate and grow stronger.
How much does it cost to do market research for a startup
At Purrweb, it costs from $1,000 to $3,000 and depends on the scale of research. If you want a personalized figure, don’t hesitate to contact us in the form below. Our estimate also includes fleshing out the startup idea and the market research itself. These factors go hand-in-hand. Let’s take a closer look at them:
Fleshing out the startup idea. This process makes market research easier. If the startup idea isn’t concrete, it’s difficult to know what to look out for.
Imagine you’re creating a food delivery app. It’s a very broad category with a wide audience. Who should be picked out to conduct interviews with? And who should receive your questionnaires?
If we’re talking about secondary market research, this process becomes even more vital. Entrepreneurs can spend a lot of time gathering and analyzing data online which is ultimately irrelevant. If they would have fleshed out their startup idea, they would know what data is useful. Instead of scouring the internet for hours, they could quickly pick appropriate research without overthinking it.
Market analysis. This step includes analysis of the information you’ve collected yourself. If you’re just starting out, we’ll arrange detailed market research on our own. Here’s what it includes:
-
- Secondary market research. We use it to get a general understanding of the market we’re dealing with.
- Target audience analysis. We distinguish general patterns your potential users rely on. At the same time, we outline their key characteristics: age, gender, likes and dislikes, etc.
- Primary market research. We pick out members of your target audience and conduct interviews — do qualitative research.
- Data interpretation. We look at the findings, pick out trends, and figure out how to go forward with development.
What to do with the market research results
Interpreting data correctly is key to a startup’s success. Here’s how to do it right:
Outline key trends. Take primary market research. If some respondents’ answers overlap, you can take it into account when creating your app.
Imagine a food delivery app. If the audience members say they value transparency, include features that make it easier to track orders. You can integrate a screen which shows the stages of order preparation. Users can check it out to see if the courier has already picked up the food or not.
Be wary of false-positives. This relates to interviews. Make sure that the questions remain open-ended. If they’re not, it’s possible to skew the answers in the wrong direction. These kinds of answers aren’t realistic. If the startup is based on them, chances are it won’t succeed.
What does decent market research look like: case studies
At Purrweb, we use target audience analysis regularly. It’s a key part of our development process. We used it while creating a mental health app and a healthcare app. Let’s take a closer look at them:
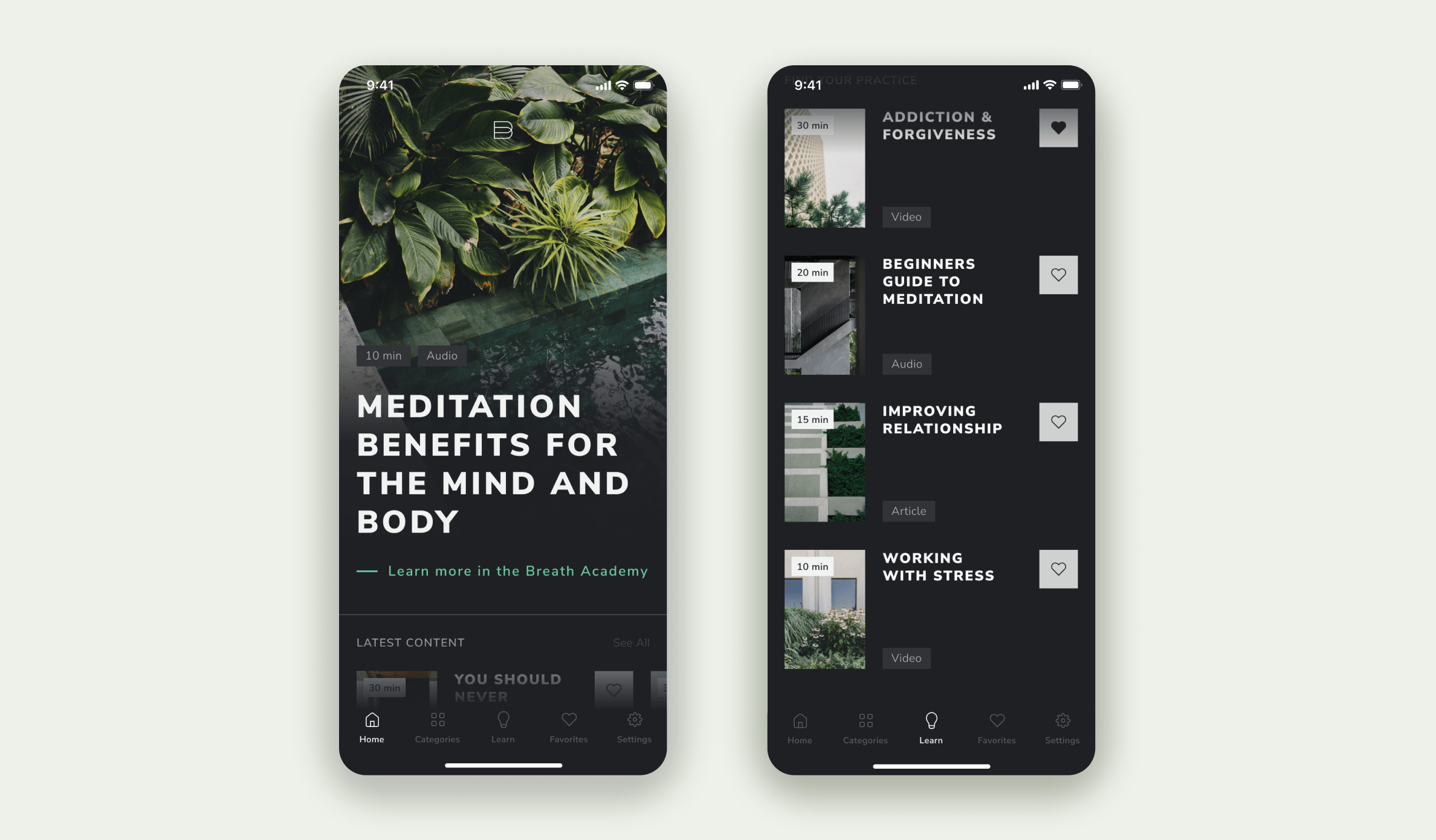
Breathmethod. A meditation app for people who never dealt with healing practices, but want to try them out.
We outlined the key demographic and their wants. These are people who’ve grown tired of big city life and its rapid pace. They’re depressed, exhausted, and somewhat anxious. These people want to get in tune with themselves, and they believe meditation to be a good way to do that.
Market research includes competitor analysis — that’s what we did in this case, too. We picked out 6 apps in the same niche, outlined their strengths and weaknesses. We later perfected the things they lacked.
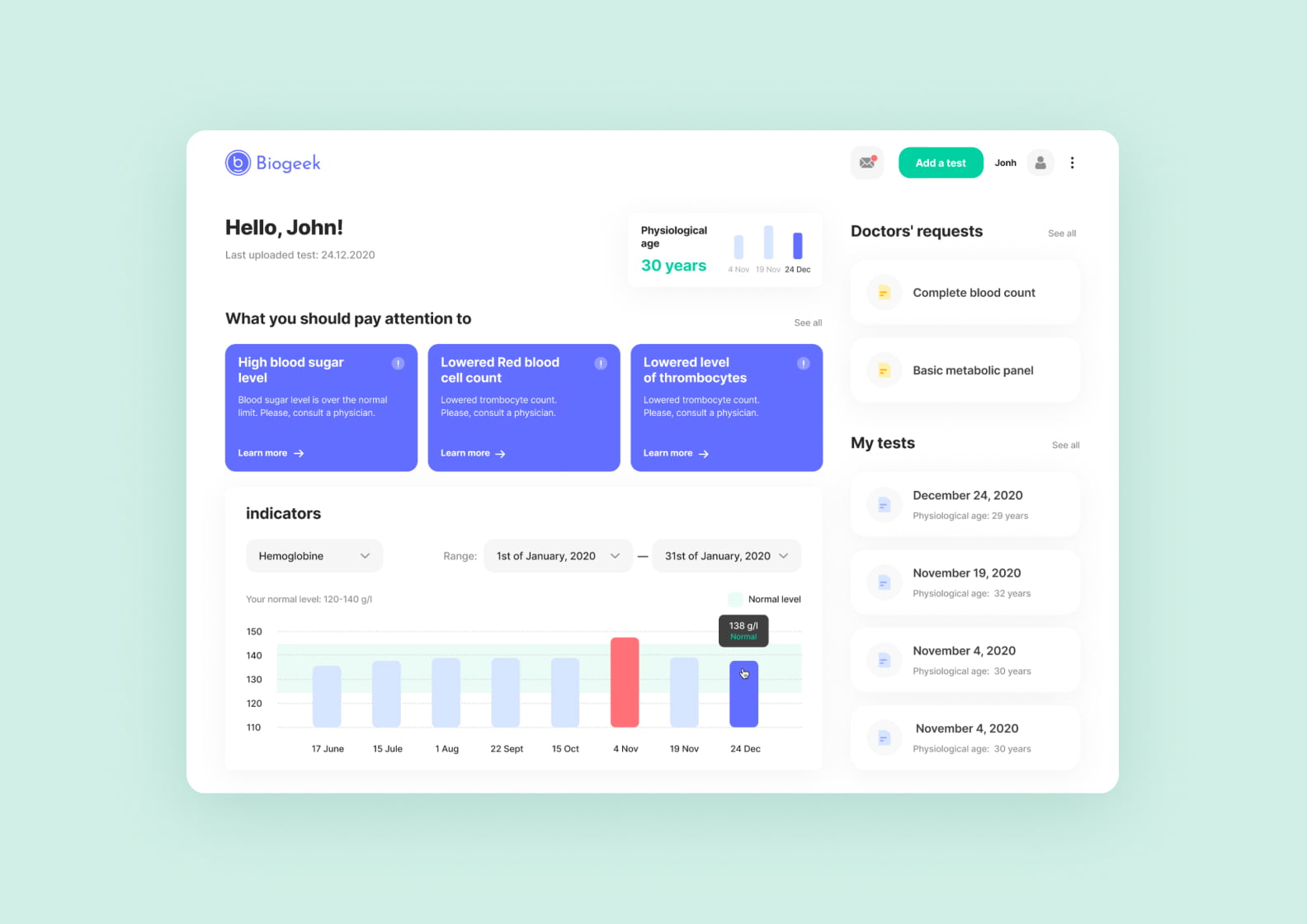
Biogeek. An app that helps monitor lab results and track key health markers.
We analyzed the target audience — these are people who’re scrupulous about their health. They want to know what happens to their bodies in full detail.
With this info in mind, we outlined key features we wanted to include. Users can input their personal data, track lab tests, and get recommendations regarding their health.
What comes next?
So you’ve conducted market research for the startup, then what’s the next step? The MVP, of course! Rely on Purrweb’s expertise and we’ll make it for you. Whether it’s a booking app, a food delivery app, a copy trading platform, or mental health service, we’ve done it before and can do it again for you.
Contact us for all the details.